Part of a two-article series, this article looks at the health issues that arise from using computers. To read the article about safety issues when using a computer click here.
There are many jobs that require the employee to work at a computer for several hours a day, or their whole shift. It’s a fundamental fact that human beings aren’t designed to sit behind a screen making small movements with our hands for 9 hours a day, and the prolonged use of computer equipment can be detrimental to our health.
The use of computer equipment
Muscles, bones and posture
Often the main risks to health and safety from the use of IT equipment and computers comes from the musculoskeletal and eye health issues that can occur from improper use, or poor management of the use of computer equipment.
A poor typing position and posture can lead to strain in the upper back, shoulders, lower back and more muscles. This may lead to issues with your posture, the alignment of your spine or cause your shoulders to round and your back to hunch. Discomfort while typing, such as a soreness in the neck or shoulders can be an indicator that somethings wrong, if ignored this can then result in muscular or skeletal problems which are very painful.
Common computer injuries (typing & clicking)
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
The repeated use of a body part can result in repetitive strain injury. In the case of using computers, this will most likely be in the forearms, wrists, hands and fingers.
An example of an RSI is tendonitis – every time that you move or flex your fingers, the tendons in your arms will move too. This isn’t typically an issue; however, a poor typing position and prolonged typing can cause the tendons to be overworked and weaken resulting in pain and potential injuries.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when the nerve inside of your wrist is squeezed by your carpal tunnel. This is common if you are frequently bending your wrist (such as to type) or you are overweight (which can be common with office workers as you don’t tend to move for 9 hours a day).
Eyestrain, headaches and difficulties concentrating can all stem from over-use of computer equipment. These will all affect health and therefore performance at work:
- Eye strain – The human eye is not intended to spend 8:30 hours plus staring at a small lines and dots on a screen. A lot of use of computers is conducted at short distances and will require the eye to focus for extended periods of time, this can lead to eye-strain and blurry vision.
- Headaches – Similarly, the consistent concentration or focusing and un-focusing of the eye can lead to headaches.
- Concentration – Our mental ability to focus on challenging, complex or monotonous tasks is a finite resource that can easily run out. Working solely in a knowledge-based role, where typing, clicking, counting and creating are your primary tasks all being completed in front of a screen, people can easily get bored.
Laptops
The issues with the use of laptops can vary from the use of computers. Typically issues result from poor posture while using the device.
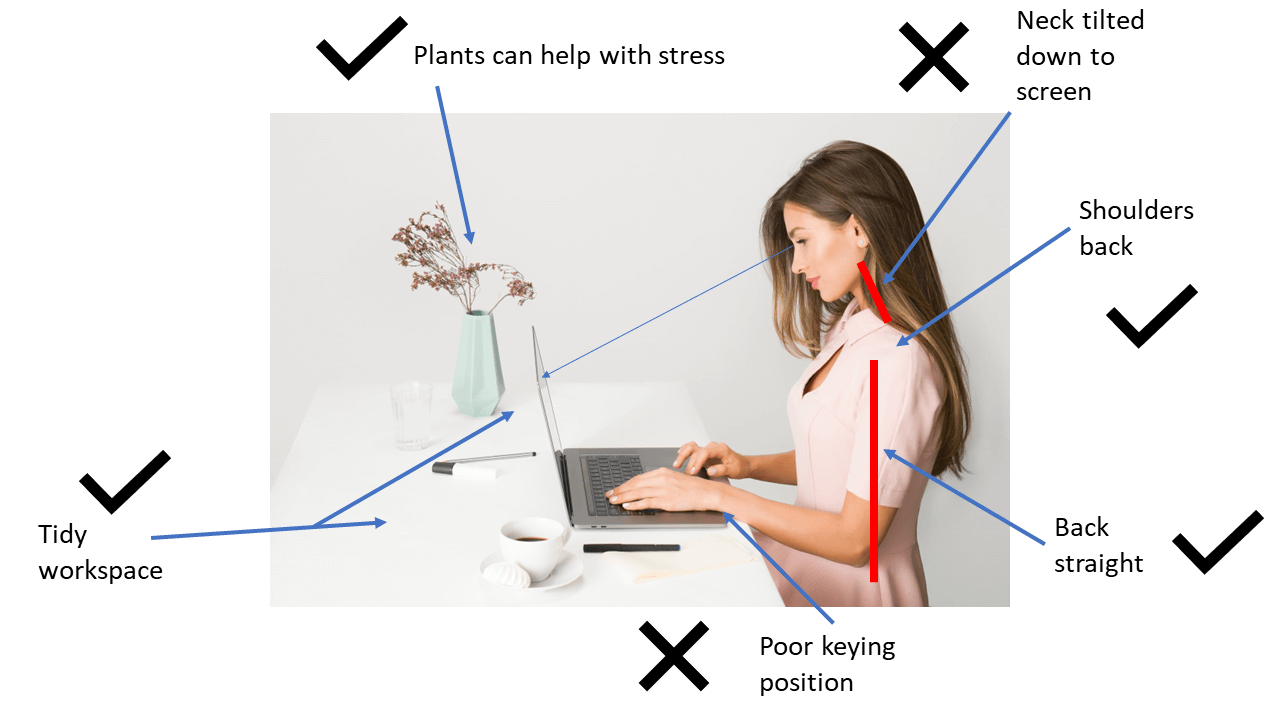
As you can see from this diagram, when using a laptop it’s important to ensure that your back is up straight and that you have enough space to rest your arms and find a comfortable keying position. Additionally, with a static computer monitor, the top of the monitor should be in line with your eyes. When using a laptop regularly for periods longer than an hour, such as if your laptop is part of a hot-desking or working from home work station, you should ensure that you follow the same guidance as using a normal PC set-up.
Additional risks associated with laptops
Power leads, fire risk – The power supply for a laptop draws a lot of energy through a transformer which is used to change the current from the alternating current inside your house to direct current that the laptop uses. This process can create a lot of heat, so if the transformer is faulty or damaged, the risk of a fire is greatly increased.
Batteries – Laptops, especially modern laptops, often employ lithium-ion batteries, or batteries designed to imitate the properties of lithium. If they become damaged, are created with a fault, or are impacted (e.g. dropping the laptop), the damage can cause the battery to rupture or become unstable. Once unstable the battery begins to generate massive amounts of heat, so much so that it can use the plastic encasing it as fuel, creating a fire.
Once this occurs, there is often no way to extinguish the battery without fully submerging it in water, which will destroy your hard drive.
Vents/cooling – If the ventilation on a laptop becomes blocked, whether by build-ups of dust and other materials, or because the vent is obstructed, the equipment and additionally the battery can become very hot. This can provide enough heat that a fire can start, especially when the laptop is blocked by thin cloth such as a bedding, or placed on-top of paper.
Theft/violence – Laptops can be valuable and being portable they can provide a tempting target for criminals. Additionally, if you’re carrying a laptop bag, the likelihood is that there is a laptop inside, this means that you don’t just have to have a laptop on show to signify that you’re a potential target to rob.
Display Screen Equipment Regulations
The UK’s Health and Safety executive have written good guidance on how to use Display Screen Equipment (DSE) in a workplace setting. This guidance includes a checklist-based risk assessment of all of the issues to look at to avoid becoming injured or experiencing ill health as a result of using DSE.
Alternatively, read more on the ACT website! We have more on this topic in our article How To Safely Use Display Screen Equipment (DSE) In The Workplace?.